VMware DRS
- markjramos
- Jul 1, 2022
- 2 min read
Updated: Jul 5, 2022

VMware DRS (Distributed Resource Scheduler) is a utility that balances computing workloads with available resources in a virtualized environment. The utility is part of a virtualization suite called VMware Infrastructure 3.
With VMware DRS, users define the rules for the allocation of physical resources among virtual machines (VMs). The utility can be configured for manual or automatic control.
VMware resource pools can be easily added, removed or reorganized. If desired, resource pools can be isolated between different business units. If the workload on one or more virtual machines drastically changes, VMware DRS redistributes the virtual machines among the physical servers. If the overall workload decreases, some of the physical servers can be temporarily powered-down and the workload consolidated.
DRS functionality
VMware DRS runs within the VMware vCenter Server to automatically balance the memory load on all virtual machines within a cluster. DRS intelligently allocates resources and can be configured to automatically take care of workload Migration (with VMotion) or assign migrations based on rules defined by an administrator.
Using resource pools that combine multiple host resources into one, DRS enables optimal workload distribution on virtual machines based on business needs and changing priorities. DRS migrates VMs based on the availability and utilization of CPU and memory resources.
When an increased VM load is encountered, DRS evaluates its priority against resource allocation rules and redistributes VMs so that capacity is dedicated to the highest-priority applications.
DRS increases productivity by allowing one administrator to monitor a large pool of resources. DRS also reduces maintenance downtime. When a physical server is put into maintenance mode, DRS automatically migrates all VMs to other servers.
DRS configuration
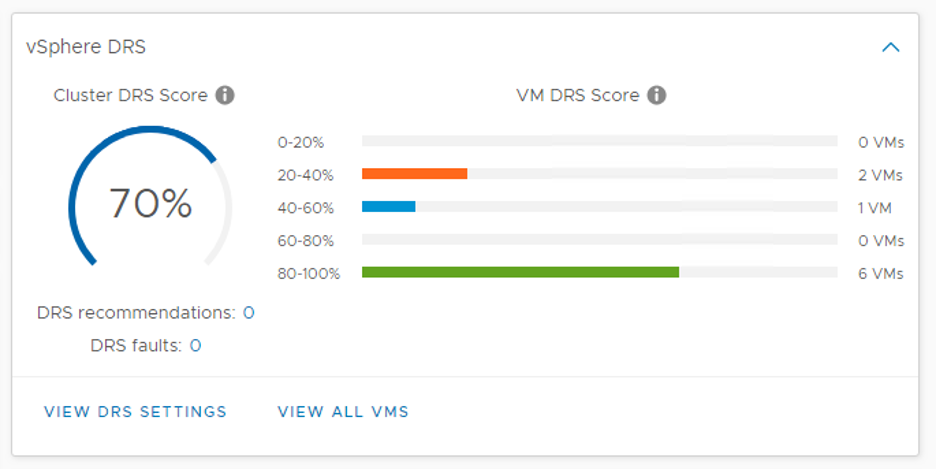
DRS can be set up in a cluster either during or after initial setup. To enable DRS, the user simply chooses the cluster name, clicks configure -> vSphere -> vSphere DRS and sets the various parameters.
Requirements:
o The VM cluster must have shared storage
o The cluster must be part of a Storage vMotion network
o vSphere Enterprise or Enterprise Plus License (more on VMware, vCenter and vSphere licensing and pricing)
o CPU compatibility or Enhanced vMotion compatibility (EVC)
o Automation options
Manual - requires the user to provide placement and migration recommendations (rules)
Partially automated - DRS provides migration recommendations -- user interaction is required to apply those recommendations
Fully automated - DRS checks for imbalanced clusters or loads and adjusts automatically -- no user interaction is required
Migration threshold
The migration threshold is where a user determines how aggressively or conservatively they want DRS to run. Most businesses choose a middle/moderately aggressive setting. Choosing the highest migration threshold will cause DRS to move VMs extremely often -- which could result in performance issues -- while choosing the lowest setting could cause VMs to move too late.
Predictive DRS
Introduced in vSphere 6.5, Predictive DRS leverages information from vRealize Suite operations to provide better placement, load balancing and resource contention prevention. Predictive DRS enables the user to mitigate potential host failures. A user can enable Predictive DRS in the vSphere cluster settings by selecting DRS -> Predictive DRS and checking the checkbox




Comments